In today’s fast-paced digital world, managing your computer’s power efficiently is essential for optimal performance and convenience. If you’ve ever faced the frustration of waking your Windows PC from sleep mode, only to discover it’s drained its battery, you might want to consider the often-overlooked hibernation feature. Hibernation allows your system to save its current state to your storage drive, enabling a quick restart without the worry of battery loss, making it an excellent solution for users on the go. This introduction will explore what hibernation is, how it differs from sleep and shutdown, and the best practices for utilizing this helpful feature.
| Feature/Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Hibernation | A power state that saves the current system state to the storage drive, allowing for a faster boot up. |
| Difference from Sleep | In sleep mode, the PC consumes some battery, while hibernation saves the state and shuts down completely. |
| Fast Startup | Uses hibernation technology to speed up boot times by saving system kernel and drivers. |
| When to Hibernate | Best used when you won’t be using the PC for a while and want to save battery, like during travel. |
| Frequency of Hibernation | Frequent hibernation can lead to junk files accumulating, but is generally safe if not done excessively. |
| Hiberfil.sys File | The file that saves the hibernation state, which may grow in size over time and can cause issues. |
| Best Practice | It’s recommended to periodically restart or shut down the PC to maintain performance and prevent issues. |
Understanding Hibernate Mode
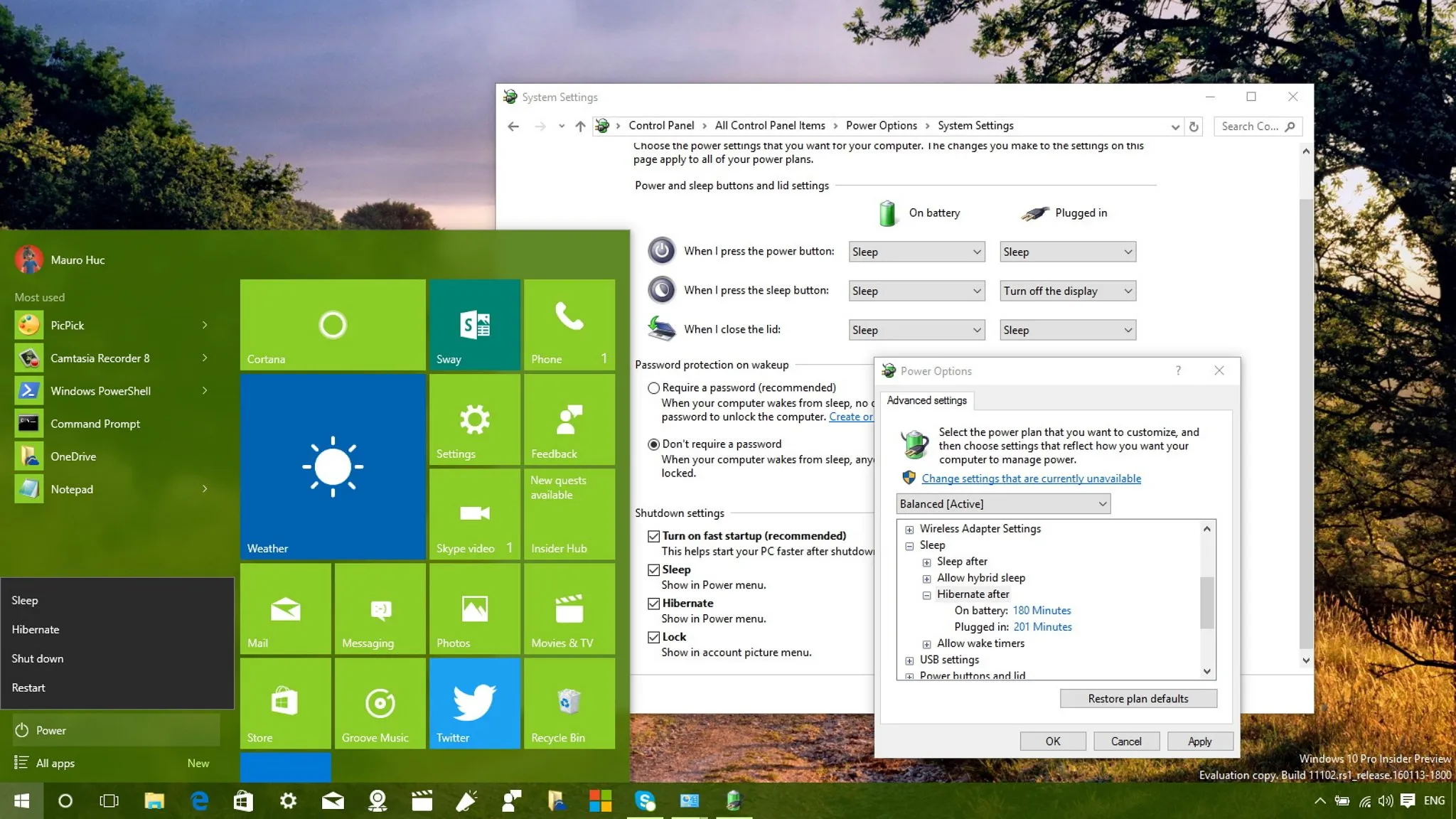
Hibernate mode is a special power state for Windows PCs that saves your current work and settings without using any battery. When you choose to hibernate, your computer saves everything into a special file on your hard drive called Hiberfil.sys. This allows your PC to power down completely, meaning it won’t use any electricity, unlike sleep mode which still consumes battery. When you turn your computer back on, it quickly restores everything exactly as you left it.
This feature is especially useful when you know you won’t be using your computer for a while but want to pick up right where you left off. For instance, if you’re heading to class or running errands, hibernation lets you save your work and avoid losing battery life. It’s like putting your work in a safe place while you step away, ensuring that when you return, you’re ready to dive back into your projects without starting all over.
The Benefits of Hibernating Your PC
Hibernating your PC offers several advantages that can enhance your computing experience. First and foremost, it conserves battery life while ensuring that your work is saved. Unlike sleep mode, where your laptop still consumes power, hibernation completely powers down the machine after saving your current session. This is particularly beneficial for laptop users who frequently move between locations and want to ensure their device lasts throughout the day.
Moreover, hibernation significantly reduces boot-up times. By saving the entire system state, including open applications and documents, you can quickly resume your work without waiting for the operating system and programs to load from scratch. This seamless transition can boost productivity, especially for users who regularly switch between tasks or need to pause their work for meetings or other interruptions.
Hibernation vs. Sleep: Which Is Better for You?
When deciding between hibernation and sleep mode, it’s essential to consider your specific needs. Sleep mode is ideal for short breaks, allowing your PC to wake up almost instantly while still drawing a small amount of power. This is great for users who are stepping away for just a few minutes or want to quickly return to their work without a lengthy startup process.
On the other hand, hibernation is better suited for longer periods away from the computer. If you know you’ll be away for an extended time, like during a long flight or overnight, hibernation is the wiser choice. It ensures that your laptop’s battery doesn’t drain, allowing you to return to your exact workspace without any data loss or the hassle of reopening applications.
Troubleshooting Common Hibernation Issues
While hibernation is generally a reliable feature, users may occasionally encounter issues that disrupt their experience. For instance, if your computer fails to wake from hibernation, it could be due to outdated drivers or power settings. Ensuring that your device drivers are up to date and that your power settings are optimized can help mitigate these problems.
Another common issue is the growing size of the Hiberfil.sys file. As you hibernate your PC frequently, this file can become bloated, causing slowdowns or errors upon resuming. To resolve this, consider cleaning up unnecessary files on your system and performing a regular restart to refresh memory and clear temporary files. This maintenance can enhance your overall computing experience and help your system run smoothly.
Best Practices for Using Hibernate on Windows
To maximize the benefits of hibernating your Windows PC, it’s vital to develop good habits around its use. One best practice is to periodically shut down your computer completely. This allows your system to reset and can help prevent potential issues that arise from prolonged hibernation. Aim for a full shutdown at least once a week, depending on your usage patterns.
Additionally, monitor the size of your Hiberfil.sys file. If you notice it’s growing excessively, consider deleting it and allowing Windows to recreate it. This can free up space and ensure your hibernation process remains efficient. Lastly, stay informed about Windows updates, as these can enhance the performance and reliability of the hibernation feature.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens when I hibernate my Windows PC?
When you **hibernate** your Windows PC, it saves everything you were doing to your hard drive and then **shuts down**. When you turn it back on, it resumes right where you left off!
How is hibernating different from sleeping my computer?
**Hibernation** saves your work and turns off the computer completely, while **sleep** keeps it on in a low-power state. Sleep uses some battery, but hibernation saves battery by shutting down.
Can I use hibernate if I have Fast Startup on my PC?
Yes! If **Fast Startup** is enabled, your PC is already using hibernation. It helps your computer start faster by saving important system parts when you shut it down.
Is it safe to hibernate my PC every day?
Hibernating often is generally safe, but if you do it too much without restarting, it can slow things down. It’s good to **restart** your PC sometimes to keep it running smoothly.
What should I do if my computer starts having problems after hibernating?
If you notice issues after hibernating, try **restarting** your computer. This can fix many problems caused by hibernation and clear out temporary files.
When is the best time to use hibernation on my laptop?
Hibernation is great when you won’t be using your laptop for a while, like during a flight or class. It keeps your work safe without using battery power.
Can hibernation affect my computer’s memory or storage?
Yes, hibernation can fill up your computer’s memory with temporary files over time. To keep it healthy, remember to restart or shut down your PC now and then.
Summary
The content discusses the benefits of hibernating a Windows PC as an alternative to putting it to sleep. Hibernation saves the current system state to the storage drive, allowing for faster boot times and conserving battery power. It is particularly useful when the PC will not be used for an extended period. While some concerns exist about the impact of frequent hibernation on system performance and SSD longevity, occasional restarts can mitigate these issues. Overall, hibernation is a practical power option that can enhance productivity, especially for users on the go, as long as it is balanced with regular shutdowns.
Leave a Reply